Bulbs
Flower Basics
Flower Beds & Specialty Gardens
Flower Garden
Garden Furniture
Garden Gnomes
Garden Seeds
Garden Sheds
Garden Statues
Garden Tools & Supplies
Gardening Basics
Green & Organic
Groundcovers & Vines
Growing Annuals
Growing Basil
Growing Beans
Growing Berries
Growing Blueberries
Growing Cactus
Growing Corn
Growing Cotton
Growing Edibles
Growing Flowers
Growing Garlic
Growing Grapes
Growing Grass
Growing Herbs
Growing Jasmine
Growing Mint
Growing Mushrooms
Orchids
Growing Peanuts
Growing Perennials
Growing Plants
Growing Rosemary
Growing Roses
Growing Strawberries
Growing Sunflowers
Growing Thyme
Growing Tomatoes
Growing Tulips
Growing Vegetables
Herb Basics
Herb Garden
Indoor Growing
Landscaping Basics
Landscaping Patios
Landscaping Plants
Landscaping Shrubs
Landscaping Trees
Landscaping Walks & Pathways
Lawn Basics
Lawn Maintenance
Lawn Mowers
Lawn Ornaments
Lawn Planting
Lawn Tools
Outdoor Growing
Overall Landscape Planning
Pests, Weeds & Problems
Plant Basics
Rock Garden
Rose Garden
Shrubs
Soil
Specialty Gardens
Trees
Vegetable Garden
Yard Maintenance
How Do Plant Cells Divide?
How Do Plant Cells Divide?. Just like animal cells, plant cells undergo division through two processes called mitosis and meiosis. Sex cells or gametes are produced by meiosis, while most cells in the plant divide through mitosis.
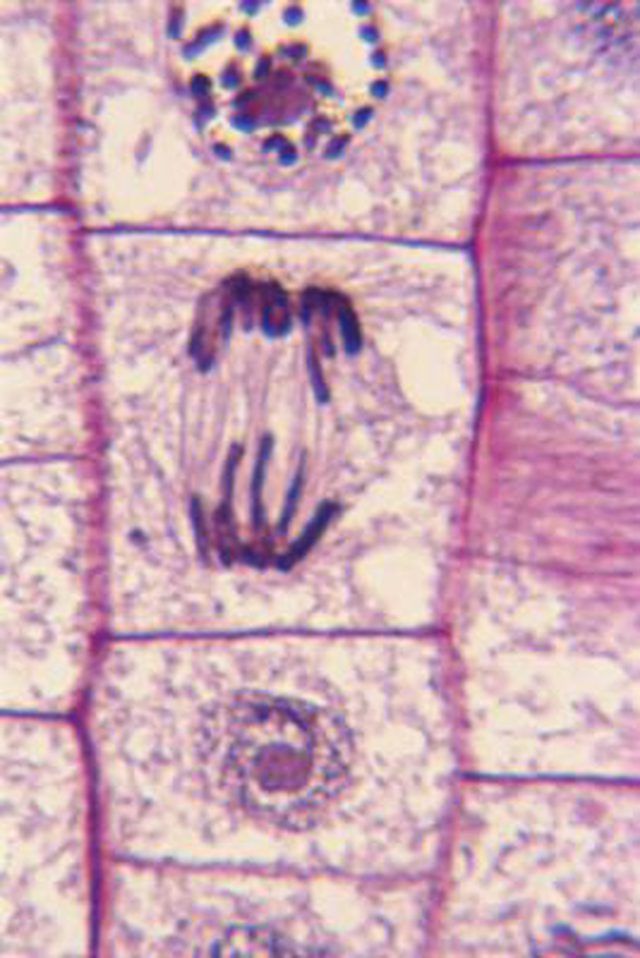
Just like animal cells, plant cells undergo division through two processes called mitosis and meiosis. Sex cells or gametes are produced by meiosis, while most cells in the plant divide through mitosis.
Types
Mitosis is divided into four phases: prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase. Meiosis, by contrast, takes place in two distinct stages, meiosis I and meiosis II. Each stage has four phases, so that meiosis I is divided into prophase I, metaphase I, anaphase I and telophase I, while meiosis II is divided into prophase II, metaphase II, anaphase II and telophase II.
Features
During both processes, the chromatin fibers of the chromosome become condensed and the chromosomes are lined up along the center of the cell by spindle fibers. The spindle fibers pull the chromosomes apart, so that half of the chromosomes go to one daughter cell and half to the other. A new cell wall forms between the two dividing cells through formation of a cell plate from sacs called vesicles.
Considerations
Meiosis and mitosis exhibit a number of crucial differences. No DNA replication takes place between meiosis I and meiosis II, so the end effect of meiosis is to create four daughter cells, each of which will have half as many chromosomes as the parent cell. During meiosis I, sections of the paternal and maternal copies of a chromosome can be exchanged to create recombinant chromosomes through a process called homologous recombination. This process increases genetic diversity in the plant's offspring and thus plays an important role in evolution.